aTTP is acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and is also known as immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP). aTTP and iTTP are the same condition. Your healthcare team may use either term.
The words that make up aTTP/iTTP help explain what is happening in the body.
Acquired means you were not born with the condition. It is something you developed later in life. The main cause is not known. Immune-mediated means the cause of the condition is not known, but it happens when the immune system isn’t working normally.
Thrombotic means blood clots form in the blood vessels. In aTTP/iTTP, small blood clots can form throughout the body.
Thrombocytopenic means having a lower number of blood platelets than you should. This happens because the platelets clump together to make blood clots throughout the body.
Purpura are purple bruises that are caused by bleeding under your skin. These bruises are a key symptom of aTTP/iTTP.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about aTTP/iTTP >
You may hear the term TTP used by your care team. TTP includes both acquired/immune-mediated TTP and hereditary or congenital TTP. Hereditary or congenital TTP is a condition people are born with that is extremely rare. Fewer than 5% of cases are hereditary.
aTTP is also known as immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP). aTTP and iTTP are the same condition. Your healthcare team may use either term.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; TTP=thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about aTTP/iTTP >
Symptoms of an aTTP/iTTP episode can include:
-
Bleeding from the gums or nose
-
Purple bruises (known as purpura) and/or red or purple dots (known as petechiae) on the skin
-
Blood in urine
-
Stomach pain
-
Chest pain
-
Seizures
-
Headaches, confusion, or distorted vision
-
Tiredness and jaundice (a yellowing of the skin and eyes)
If you think you are showing signs of an aTTP/iTTP episode, talk to your doctor or visit your local emergency room right away.
aTTP/iTTP acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about the signs of aTTP/iTTP >
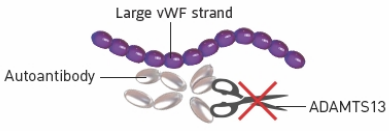
aTTP/iTTP causes 3 things to go wrong in the body
1
The immune system attacks
ADAMTS13 with autoantibodies
What it means for the body
If ADAMTS13 is being attacked, there won’t be enough in the blood
2
Because there is not enough
ADAMTS13, vWF strands don’t get cut
What it means for the body
When vWF strands grow too long, they attract a lot of platelets when they are not supposed to, which means there are not enough platelets circulating in the blood
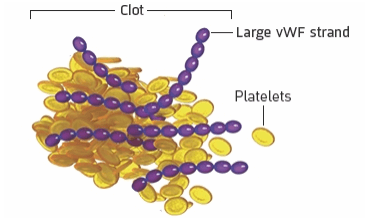
3
When long strands of vWF attract
platelets, dangerous blood clots form in small blood vessels
What it means for the body
These blood clots can cause serious health problems like stroke, heart attack, seizures, and organ damage
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vWF=von Willebrand factor.
Learn more about the signs of aTTP/iTTP >
It’s not fully understood why some people develop aTTP/iTTP—it can affect anyone.
<2000 people
aTTP/iTTP affects fewer than 2000 people in the United States every year.
30 to 50 years old
aTTP/iTTP usually affects people 30 to 50 years of age, but it can affect people of any age.
Women
aTTP/iTTP is more common in women than men.
Black ethnicity
aTTP/iTTP is more likely to affect people of Black ethnicity.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about the signs of aTTP/iTTP >
Diagnosis is normally made from a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
-
Physical examinations may show some of the common symptoms of aTTP/iTTP, such as purple bruises (known as purpura) and/or red or purple dots (known as petechiae) on the skin, blood in urine, headaches, confusion, or distorted vision
-
Diagnostic tests to evaluate platelet and red blood cell count, ADAMTS13 enzyme activity levels, and organ function
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about aTTP/iTTP >
Your doctor may perform certain lab tests to monitor your health at diagnosis and throughout an aTTP/iTTP episode.
Platelet and red blood cell count
Your doctor will confirm if you have fewer platelets and red blood cells than you should and if they are improving with treatment
ADAMTS13 enzyme activity levels
Your doctor will see how well your ADAMTS13 is working. Low levels mean aTTP/iTTP is active. Low levels can still occur during treatment and after other symptoms improve
Organ function
Because clots can impact the organs, your doctor may perform different tests to check how well your organs are working
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
The goal of treatment is to address each problem aTTP/iTTP causes in the body.
Problem caused by aTTP/iTTP
Your immune system attacks ADAMTS13 with autoantibodies
Treatment
Immunosuppressive therapy is a type of medicine that helps decrease the activity of your immune system. In aTTP/iTTP, it suppresses the production of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies
Problem caused by aTTP/iTTP
Because there is not enough ADAMTS13, von Willebrand factor (vWF) strands don’t get cut. When vWF strands grow too long, they attract a lot of platelets when they are not supposed to, which means there are not enough platelets circulating in the blood
Treatment
Plasma exchange (PEX) is a procedure that removes and replaces a person’s blood plasma over a few hours. In aTTP/iTTP, it replaces platelets and ADAMTS13 in the blood. PEX may need to be done for several days or weeks
Problem caused by aTTP/iTTP
When long strands of vWF attract platelets, dangerous blood clots may form when you don’t need them
Treatment
CABLIVI is a prescription medicine for adults, in combination with PEX and immunosuppression, designed specifically for aTTP/iTTP. It helps stop platelets from sticking to vWF and helps prevent your body from forming dangerous blood clots during an aTTP/iTTP episode
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; vWF=von Willebrand factor.
Learn more about aTTP/iTTP treatment >
Acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP) is a chronic condition that can have emergency episodes. You won’t need to take treatment every day for aTTP/iTTP forever. But after having 1 episode, it is possible to have another aTTP/iTTP episode. This is called a recurrence or a relapse. While some people may only experience 1 aTTP/iTTP episode, many others may experience a relapse. This means they may have another sudden aTTP/iTTP episode that requires therapy immediately.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about living with aTTP/iTTP >
Symptoms of an aTTP/iTTP recurrence are likely to be similar to an initial episode which can include:
-
Bleeding from the gums or nose
-
Purple bruises (known as purpura) and/or red or purple dots (known as petechiae) on the skin
-
Blood in urine
-
Stomach pain
-
Chest pain
-
Seizures
-
Headaches, confusion, or distorted vision
-
Tiredness and jaundice (a yellowing of the skin and eyes)
If you think you are showing signs of an aTTP/iTTP episode, talk to your doctor or visit your local emergency room right away.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about living with aTTP/iTTP >
CABLIVI is a prescription treatment used to treat adults with acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP*) designed to work with a procedure called plasma exchange and a medication called immunosuppressive therapy. CABLIVI, together with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy, addresses each problem aTTP/iTTP causes in the body.
*aTTP is also known as iTTP. You and your healthcare team can use either term.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about CABLIVI >
CABLIVI is a prescription treatment used to treat adults with acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP*), with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
*aTTP is also known as iTTP. You and your healthcare team can use either term.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about CABLIVI >
CABLIVI is used together with a procedure called plasma exchange and a medication called immunosuppressive therapy to treat acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP/iTTP) in adults. CABLIVI has an active ingredient called caplacizumab-yhdp (cap-luh-siz-uh-mab). It is a small protein that is meant to prevent the body from forming dangerous blood clots during an aTTP/iTTP episode.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about how CABLIVI works >
It is recommended to inject CABLIVI every day you receive plasma exchange and for 30 days after your last plasma exchange session. Your doctor may decide you need to inject CABLIVI for more than 30 days. This additional period may last up to 28 days.
Learn more about taking CABLIVI >
DAY 1
You will receive 2 doses of CABLIVI on day 1
First dose: Your care team will give the first dose of CABLIVI through an IV injection before your first plasma exchange session
Second dose: Your care team will give the second dose of CABLIVI as an injection into the skin of your stomach after your first plasma exchange session
HOSPITAL STAY
(number of days can vary)
Every day after day 1, CABLIVI will be given after each plasma exchange session as an injection into the skin of your stomach
Each person receives plasma exchange sessions for a different number of days. Your doctor will decide how many plasma exchange sessions you need
After plasma exchange is no longer needed, you will continue to receive a CABLIVI injection into the skin of your stomach daily for the remainder of your stay and prepare to inject CABLIVI at home
When your doctor decides you can safely leave the hospital, you will inject CABLIVI at home until it’s been 30 days since your last plasma exchange. Some people may need to inject CABLIVI longer (up to another 28 days), depending on their doctor’s direction.
Your CABLIVI injection can be done by you, a family member, or another caregiver. Before you leave the hospital, you and your doctor should decide who that person will be. Your care team should teach you, your family, or your caregiver how to inject CABLIVI with confidence. Let your doctor know if you, your family, or your caregiver are not comfortable or if you have any questions.
Learn more about taking CABLIVI >
CABLIVI can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them. Because CABLIVI works by stopping blood clots from forming, it may affect normal blood clotting and increase the risk of severe bleeding.
In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of nosebleed, bleeding from the gums, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, and bleeding from the uterus were each reported in 1% of people.
Learn more about possible side effects of CABLIVI >
With HemAssistTM Sanofi Support, support is available to cover the cost of CABLIVI’s co-pay or co-insurance for qualified, commercially insured patients, up to the program maximum.* CABLIVI will be provided at no cost to eligible underinsured or uninsured patients.†
*Not valid for CABLIVI prescriptions covered by or submitted for reimbursement under Medicare, Medicaid, VA, DoD, Tricare, or similar federal or state programs including any state pharmaceutical assistance programs. Not valid where prohibited by law. Savings may vary depending on the patient’s out-of-pocket costs. Upon registration, the patient will receive all program details.
†Approval is not guaranteed. Sanofi reserves the right to modify or discontinue the programs at any time without notice.
Learn more about patient assistance >
Every insurance plan is different, so you will need to contact your insurance company to learn about your coverage options.
With HemAssist, support is available to cover the cost of CABLIVI’s co-pay or co-insurance for qualified, commercially insured patients, up to the program maximum.* CABLIVI will be provided at no cost to eligible underinsured or uninsured patients.†
*Not valid for CABLIVI prescriptions covered by or submitted for reimbursement under Medicare, Medicaid, VA, DoD, Tricare, or similar federal or state programs including any state pharmaceutical assistance programs. Not valid where prohibited by law. Savings may vary depending on the patient’s out-of-pocket costs. Upon registration, the patient will receive all program details.
†Approval is not guaranteed. Sanofi reserves the right to modify or discontinue the programs at any time without notice.
Learn more about patient assistance >
You can receive additional education and resources in 2 ways:
-
Enroll in HemAssist to be connected with a dedicated team that will work together seamlessly to help manage your aTTP/iTTP care.
-
Fill out our sign-up form to stay informed about CABLIVI and aTTP/iTTP.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about patient assistance >
For questions specific to your treatment and how you are doing, talk to your doctor.
For questions about HemAssist Sanofi Support for Cablivi, call 1-833-723-5463 Monday – Friday 8 AM to 7 PM ET.
Learn more about patient assistance >
Taking CABLIVI once a day is important for successful treatment. However, if you miss a dose, do the following:
-
During your plasma exchange sessions: Inject CABLIVI as soon as possible
-
After you’re no longer on plasma exchange: Inject CABLIVI daily within 12 hours of your scheduled time. After 12 hours, skip the dose and inject the next scheduled dose
You should inject only one (1) dose of CABLIVI at a time, as recommended by your doctor. If you have accidentally used more than this, don’t inject any more and call your doctor right away.
Do not stop treatment early without talking with your doctor, even if you start to feel better. Stopping treatment too early may result in another aTTP/iTTP episode.
aTTP/iTTP=acquired/immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Learn more about taking CABLIVI >
CABLIVI, in combination with PEX and immunosuppression, can help you take on aTTP/iTTP with confidence
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
Who should not take CABLIVI?
Do not take CABLIVI if you’ve had an allergic reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of the ingredients in CABLIVI.
What should I tell my healthcare team before starting CABLIVI?
Tell your doctor if you have a medical condition including if you have a bleeding disorder. Tell your doctor about any medicines you take, including medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
Talk to your doctor before scheduling any surgery, medical or dental procedure.
What are the possible side effects of CABLIVI?
CABLIVI can cause severe bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of nosebleed, bleeding from the gums, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, and bleeding from the uterus were each reported in 1% of subjects. In the post-marketing setting, cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI. Contact your doctor immediately if symptoms of excessive bruising, excessive bleeding, or major bleeding occur. Signs and symptoms of bleeding include: pain, swelling or discomfort, prolonged bleeding from cuts, increased menstrual flow or vaginal bleeding, nosebleeds, bleeding of gums from brushing, unusual bleeding or bruising, red or dark brown urine, red or tar black stools, headache, dizziness, or weakness.
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you have a bleeding disorder (i.e. hemophilia) or if you take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
CABLIVI should be stopped for 7 days before surgery or any medical or dental procedure. Talk to your doctor before you stop taking CABLIVI.
The most common side effects include nosebleed, headache and bleeding gums.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of CABLIVI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
What is CABLIVI?
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of adults with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
Who should not take CABLIVI?
Do not take CABLIVI if you’ve had an allergic reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of the ingredients in CABLIVI.
What should I tell my healthcare team before starting CABLIVI?
Tell your doctor if you have a medical condition including if you have a bleeding disorder. Tell your doctor about any medicines you take, including medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
Talk to your doctor before scheduling any surgery, medical or dental procedure.
What are the possible side effects of CABLIVI?
CABLIVI can cause severe bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of nosebleed, bleeding from the gums, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, and bleeding from the uterus were each reported in 1% of subjects. In the post-marketing setting, cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI. Contact your doctor immediately if symptoms of excessive bruising, excessive bleeding, or major bleeding occur. Signs and symptoms of bleeding include: pain, swelling or discomfort, prolonged bleeding from cuts, increased menstrual flow or vaginal bleeding, nosebleeds, bleeding of gums from brushing, unusual bleeding or bruising, red or dark brown urine, red or tar black stools, headache, dizziness, or weakness.
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you have a bleeding disorder (i.e. hemophilia) or if you take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
CABLIVI should be stopped for 7 days before surgery or any medical or dental procedure. Talk to your doctor before you stop taking CABLIVI.
The most common side effects include nosebleed, headache and bleeding gums.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of CABLIVI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
What is CABLIVI?
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of adults with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION AND INDICATIONS
Who should not take CABLIVI?
Do not take CABLIVI if you’ve had an allergic reaction to caplacizumab-yhdp or to any of the ingredients in CABLIVI.
What should I tell my healthcare team before starting CABLIVI?
Tell your doctor if you have a medical condition including if you have a bleeding disorder. Tell your doctor about any medicines you take, including medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
Talk to your doctor before scheduling any surgery, medical or dental procedure.
What are the possible side effects of CABLIVI?
CABLIVI can cause severe bleeding. In clinical studies, severe bleeding adverse reactions of nosebleed, bleeding from the gums, bleeding in the stomach or intestines, and bleeding from the uterus were each reported in 1% of subjects. In the post-marketing setting, cases of life-threatening and fatal bleeding were reported in patients receiving CABLIVI. Contact your doctor immediately if symptoms of excessive bruising, excessive bleeding, or major bleeding occur. Signs and symptoms of bleeding include: pain, swelling or discomfort, prolonged bleeding from cuts, increased menstrual flow or vaginal bleeding, nosebleeds, bleeding of gums from brushing, unusual bleeding or bruising, red or dark brown urine, red or tar black stools, headache, dizziness, or weakness.
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you have a bleeding disorder (i.e. hemophilia) or if you take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding such as anti-coagulants and anti-platelet agents.
CABLIVI should be stopped for 7 days before surgery or any medical or dental procedure. Talk to your doctor before you stop taking CABLIVI.
The most common side effects include nosebleed, headache and bleeding gums.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of CABLIVI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
What is CABLIVI?
CABLIVI (caplacizumab-yhdp) is a prescription medicine used for the treatment of adults with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP), in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Instructions For Use
Sharps Medical Waste Disposal (PDF)
Learn more about Sanofi’s commitment to fighting counterfeit drugs.